The Sierra Madre Oriental Orocline: Paleomagnetism of the Nazas Province in NE Mexico
 Orocline in the Sierra Madre Oriental
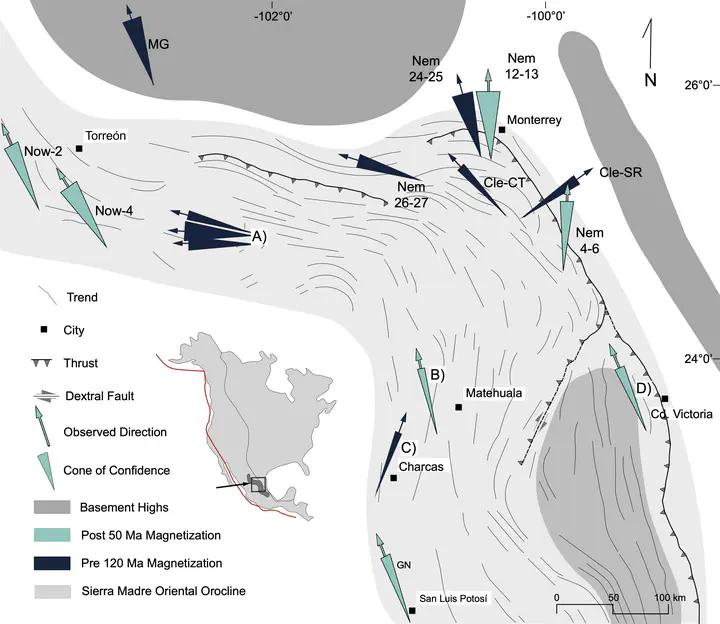
Orocline in the Sierra Madre OrientalAbstract
Curved mountain belts are spectacular natural features that contain crucial 3D information about the tectonic evolution of orogenic systems in the absence of other kinematic markers. The Mesozoic units exposed in the Mexican Fold and Thrust Belt in northeastern Mexico show a striking curvature, whose kinematic history has not been studied. The existing tectonic models of the region simply assumed the shape of the tectonic units as an inherent feature to the orogen. We investigated the kinematic history of this curvature through paleomagnetism and rock magnetism analyses, coupled with an exhaustive review of available published literature. The studied data sets indicate a protracted history of (re)magnetizations that occurred during the Late Jurassic-Paleocene times at least during the Late Jurassic, Cretaceous and early Eocene. More significantly, they show significant counterclockwise rotations in the northern flank of the curvature and moderate clockwise vertical axis rotations along its southern flank. This data set suggests that the Sierra Madre Oriental was a linear belt that experienced oroclinal bending or buckling during the Cretaceous to early Eocene period (120–50 Ma).